Extracting References Between Text and Charts via Crowdsourcing
Nicholas Kong, Marti A. Hearst, Maneesh Agrawala
Abstract
News articles, reports, blog posts and academic papers often include graphical charts that serve to visually reinforce arguments presented in the text. To help readers better understand the relation between the text and the chart, we present a crowdsourcing pipeline to extract the references between them. Specifically, we give crowd workers paragraph-chart pairs and ask them to select text phrases as well as the corresponding visual marks in the chart. We then apply automated clustering and merging techniques to unify the references generated by multiple workers into a single set. Comparing the crowdsourced references to a set of gold standard references using a distance measure based on the F1 score, we find that the average distance between the raw set of references produced by a single worker and the gold standard is 0.54 (out of a max of 1.0). When we apply clustering and merging techniques the average distance between the unified set of references and the gold standard reduces to 0.39; an improvement of 27%. We conclude with an interactive document viewing application that uses the extracted references; readers can select phrases in the text and the system highlights the related marks in the chart.
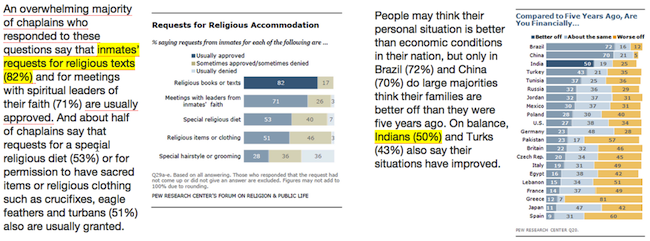
Examples of references extracted by our system, as shown in our interactive document viewing application. The user can select text (yellow background) and the application highlights the corresponding visual marks in the chart (fully saturated bars). The application also places red underlines beneath related phrases.
Research Paper
PDF (16.6M) | Interactive Document Viewer